- 4 March, 2022
- Posted by: admin
- Category: News

Emission monitoring is an urgent activity to participate in protecting and improving the environment as well as human health. Monitoring flue gas emissions limits the risk of environmental pollution. All production and business units, when operating emission-generating activities, must carry out industrial emission monitoring. Below are some detailed information explaining the concept of emission monitoring, its role and implementation process.
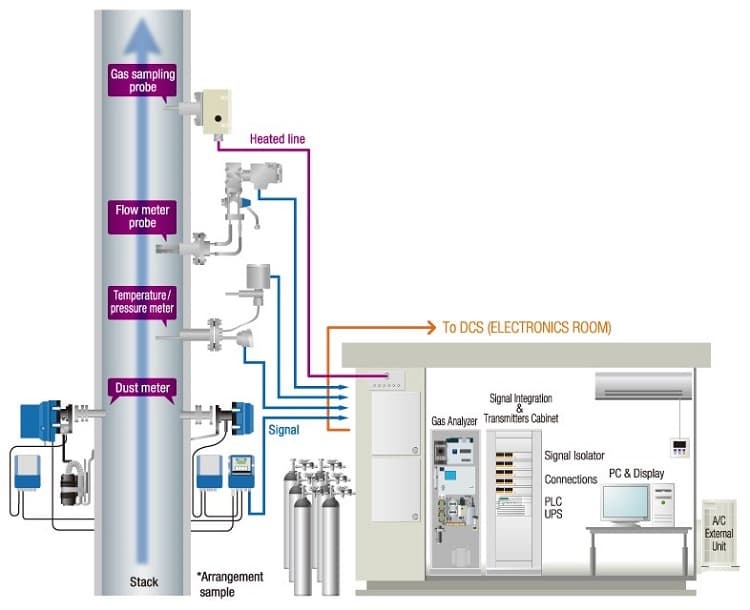
What is the concept of emission monitoring?
Emission monitoring is the process of measuring and analyzing the physical, chemical and biological parameters of the exhaust gas.
Who is responsible for monitoring chimney emissions:
Monitoring of flue gas emissions is carried out by state environmental management agencies. Individuals, units, and organizations can also conduct air environment monitoring.
What is the purpose of air monitoring?
• This is to assess whether the production units are in compliance with the standard regulations on emissions.
• The air monitoring is also to evaluate the efficiency of the production process and the exhaust gas treatment system of each unit.
• At the same time, air quality monitoring also provides data for local environmental management.
• Besides, industrial emission monitoring also helps enterprises to develop reports on the current state of the environment.
• Support state agencies to charge for environmental protection as well as for emission control.
Regulations on emission monitoring:
Objects that need to monitor chimney emissions:
• Facilities and projects on the list of large-volume emission sources specified in Appendix I and III of Decree 40/2019/ND-CP and Decree 38/2015/ND-CP
• Hazardous waste incinerators or provincial-scale solid waste treatment facilities.
• Establishments that are administratively sanctioned for discharging emissions in excess of environmental technical regulations, but repeat or repeat violations many times.
• Establishments using imported scrap as raw materials for production must make an EIA report – environmental impact assessment.
• A number of other subjects and units decided by the People’s Committee of the province.
• Thermal power plants (except natural gas fuel plants), billet production plants with a capacity of 200,000 tons/year
• Enterprises, factories producing cement, chemicals and fertilizers with an output higher than 10,000 tons/year for each type of product.
• Refinery and petrochemical factory with higher output of 10,000 tons/year
• Establishments with industrial boilers operating with a capacity of more than 20 tons of steam/hour with 1 boiler. Except for boilers that use natural gas, CNG or LPG as fuel.

Frequency of industrial emissions monitoring:
• The minimum frequency of industrial emissions monitoring is once every 3 months. The frequency of air sampling can be as low as once every 6 months or once a year but needs to be approved separately by the competent authority.
• Take samples to monitor the air environment at least 3 times/time.
Air quality monitoring time
Sampling time: air samples will be obtained when the facility is still operating normally and reaching at least 80% of its maximum capacity. Ensure the establishment is operating normally and stably during the sampling period.
Sampling time is calculated and determined according to the parameters, type of production of the establishment. According to the input material, the concentration as well as the accuracy of the analysis.
Industrial emission monitoring parameters
Based on the performance objective and the type of pulse production as an emission source, the parameters given by the emission monitoring system are different:
• Fixed environmental parameters are measured and analyzed in the field: temperature, air velocity, flow, humidity and air flow pressure inside the chimney.
• Concentration parameters of pollutants in the exhaust gas: total dust PM, residual O2, SO2, CO, NOx, H2S, COS, Pb, … Total organic substances excluding methane, Ba, HBR, HF, hcl, Cl2,Sb, As, Be, … aromatic polycyclic hydrocarbon compounds.
• Industry-specific environmental parameters: determined based on pollution parameters specified in current documents and regulations.
The process of emission monitoring includes:
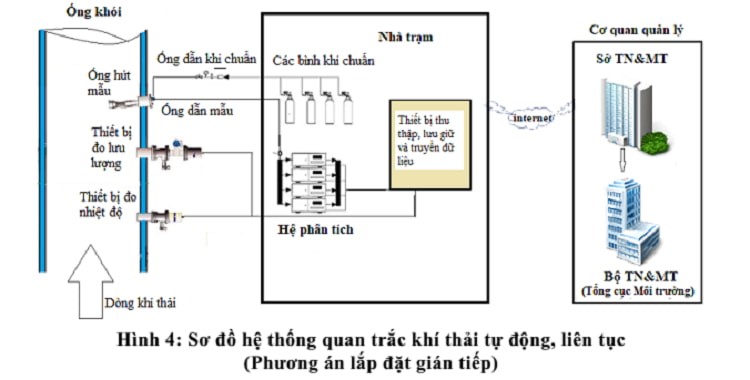
Determine location and number of points to monitor flue gas emissions
• It is necessary to determine the air environment monitoring parameters for that base object
• Determine air quality monitoring time, frequency and quantity of air quality monitoring samples
• Make a detailed industrial emission monitoring plan
• Carrying out the emission monitoring process: prepare all the contents related to the monitoring including air monitoring in the field and analysis in the laboratory.
• Prepare reports, data and assessments to report to competent agencies for consideration.
The above is an overview of chimney emission monitoring, if you have any questions or support, please leave a comment.
